Ed's
AV Handbook
Batting Practice for the AV Professional
and primer for the novice
Chapter 1 Page 1
AV Terminology
What is stereo?
Too many of our AV brethren do not understand fundamental
AV terms. I have confronted many for decades with this simple
question, "What is stereo?"
I am driven crazy by the answers I continue to receive. In an attempt to ensure what's left of my sanity, please review the following terms. We may meet on the street someday.
I am driven crazy by the answers I continue to receive. In an attempt to ensure what's left of my sanity, please review the following terms. We may meet on the street someday.
High Fidelity Audio
High fidelity refers to the accurate reproduction of recorded sound. High fidelity adheres to accurate standards such as flat frequency response, high signal-to-noise ratio, maintained phase, and a low percentage of many types of distortion measurement.* But High Fidelity can also be framed by two questions. Does the reproduced sound of a piano sound like a real piano? Does the audio system faithfully reproduce the artist's intent?*Handbook Note: Select this link Rane for a comprehensive list of audio measurement.
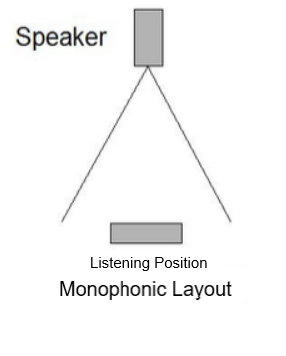
Monophonic Audio
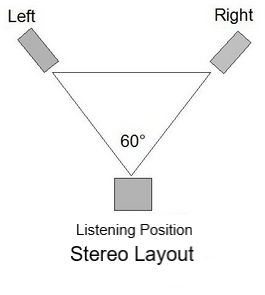
Stereo Audio
Stereo audio employs two separate audio channels via two
speakers placed in an equilateral triangle with a
listener. This arrangement creates a three-dimensional
illusion or image of musicians on a stage of height, width,
and depth. For example, drummer center rear, vocalist
center front, bass player front right, guitar front left, and
an array of background singers behind the drummer.
If a stereo audio system meets high fidelity standards, it's
referred to as a high fidelity stereo audio system.




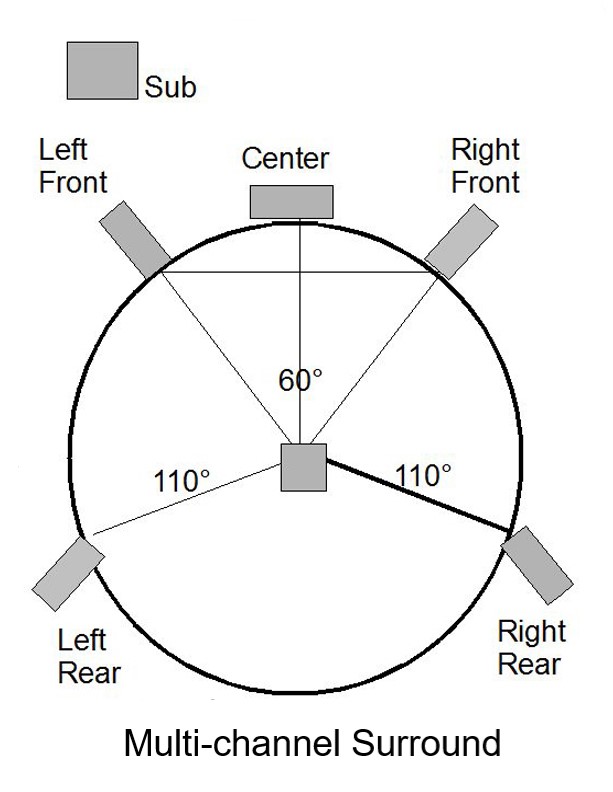
Multi-channel Surround Sound
Surround sound introduces additional channels and speakers onto the stereo arrangement. Surround sound is a circular arrangement of four, five, six, seven, or more channels of audio that surround the listener in an extended illusion of staged music or a movie soundtrack envelope of sound effects. Surround sound formats are detailed later in this chapter.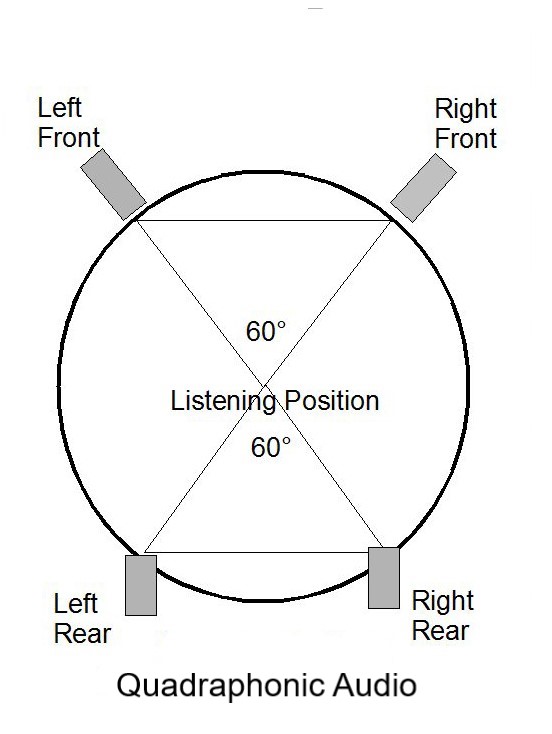
NTSC
Some joked NTSC was an acronym for never twice the same color. However, the National Television Standards Committee established the original now-retired U.S. television analog broadcast standard. Chapter four offers a detailed explanation of the NTSC broadcast standard.ATSC
The Advanced Television System Committee set the U.S.
digital broadcast standards of 8K UltraHD, UltraHDTV,
HDTV, EDTV and SDTV.

NextGenTV
ATSC 3.0 NextGenTV is the new UltraHD and 8K UltraHD U.S.
broadcast standard. NextGenTV also provides bandwidth
for wireless Internet.
Chapter four provides more detail.
Chapter four provides more detail.
HDTV
High Definition Television, expands video resolution and
the color gamut well beyond NTSC TV. HDTV offers two
versions: 1080 lines by 1920 pixels per line,
and 720 lines by 1280 pixels per line. Chapter four discusses HDTV, resolution, and color gamut in detail.
and 720 lines by 1280 pixels per line. Chapter four discusses HDTV, resolution, and color gamut in detail.
UltraHDTV
UltraHDTV (UHD1) commonly referred to as 4K, increases
video resolution and expands color gamut beyond
HDTV.
UltraHD offers 2160 lines by 3840 pixels per line. UltraHD is also discussed in great detail in chapter four.
UltraHD offers 2160 lines by 3840 pixels per line. UltraHD is also discussed in great detail in chapter four.

8K UltraHD
Although UHD 8K TVs are available, 8K programing sources are scarce.
Ed's AV Handbook
Copyright 2007 Txu1-598-288
Revised 2024
Sponsored By
Architectural
Speaker Tuning System
for
in-wall/ceiling custom installed speakers.
Reclaim the performance you paid for.
Site Menu
Home
Table of
Contents
AV
News & Blog
Handbook Chapters
1 AV
Terms
2 AV Physics
3 Sound Reproduction
4 Video Reproduction
5 The AV System Sequence
6 The Room, Speaker, & TV
7 Acoustical Strategy - Small Room
8 Home Theater by Design
9 AV Sales Training
10 AV Business & Marketing
Contact
About

